43 how do you label acceleration
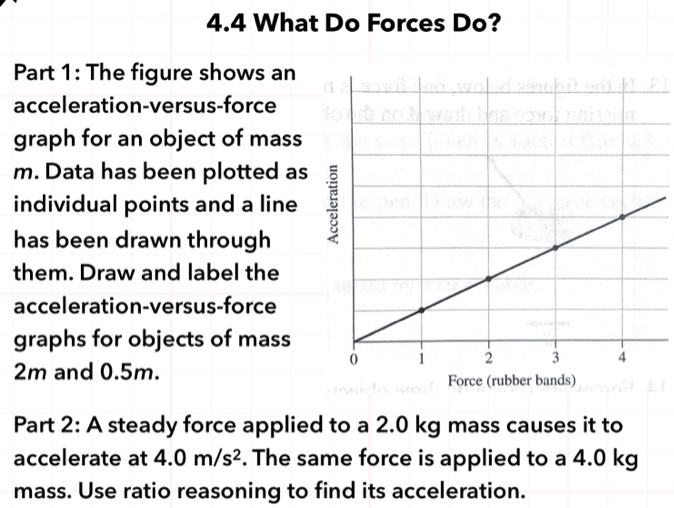
What are acceleration vs. time graphs? (article) | Khan Academy Multiplying the acceleration by the time interval is equivalent to finding the area under the curve. The area under the curve is a rectangle, as seen in the diagram below. The area can be found by multiplying height times width. The height of this rectangle is 4, and the width is 9 s. So, finding the area also gives you the change in velocity. Polyhedron Physics | Polyhedron Physics + | Virtual Online … 9 New Simulations Available! Polyhedron Learning Media is pleased to announce the release of nine NEW Polyhedron Physics simulations, including a NEW Physical Optics and Nuclear Physics Bundle. These simulations have been added to the original set and can be used by those with a subscription to Polyhedron Physics, at no additional cost.. Conservation of Energy on the Air …
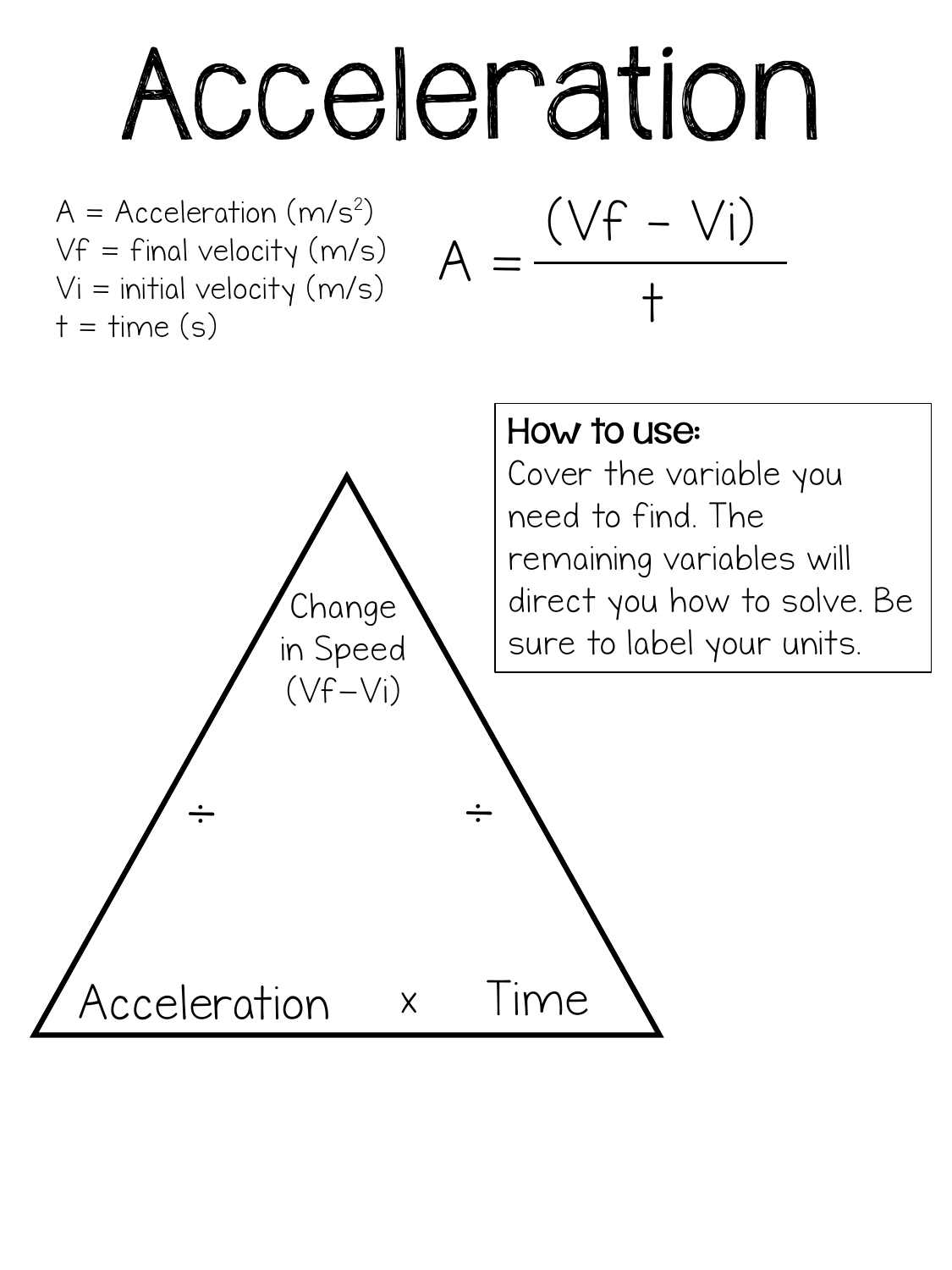
The Acceleration Formula (Equation) In Physics: How To Use It Summary. In summation, acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time and the formula expressing the average velocity of an object can be written as: a =Δ v/ Δt. The other 4 equations: d = vit+ (1/2) at2. vf = vi + at. vf = vi +2 ad. d = ( ( vi + vf )/2) t.
How do you label acceleration
How to calculate tangential acceleration - 650.org How do you label tangential acceleration? Notations Used In The Formula a t is the tangential acceleration. Δv is the change in the angular velocity. Δt is the change in time. v is the linear velocity. s is the distance covered. t is the time taken. How do you convert tangential acceleration to angular acceleration? at=rΔωΔt a t = r Δ ω Δ t . Spacecraft propulsion - Wikipedia Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry.. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Acceleration - Physics Classroom The average acceleration ( a) of any object over a given interval of time ( t) can be calculated using the equation This equation can be used to calculate the acceleration of the object whose motion is depicted by the velocity-time data table above. The velocity-time data in the table shows that the object has an acceleration of 10 m/s/s.
How do you label acceleration. Acceleration Formula With Solved Examples - BYJUS Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity to the change in time. It is denoted by symbol a and is articulated as- The S.I unit for acceleration is meter per second square or m/s 2. If t (time taken), v (final velocity) and u (initial velocity) are provided. Then the acceleration is given by the formula Where, Final Velocity is v What is acceleration? Flashcards | Quizlet What is Acceleration? It shows the constant rate of change in velocity. How do you label acceleration? M/s. What's final velocity? The velocity of an object at the end of a predetermined period of time. BDO Horse Breeding & Exchange: How to Gain Tiers | GrumpyG 19.12.2021 · Horse Breeding Tip: View the Stable locations of your horses by opening your world map (M) and clicking the city then click the horse icon at the bottom right.You can also view your horse’s location at the Stable Keeper. Breeding Timer: The 6 hour wait between breeding attempts was removed in June 2018. Horse Deaths: March 28, 2018 patch notes state that … PDF 4a. Graphing the Data: Label each axis on your graph paper in terms of ... In this Investigation, you will rely on information you have learned from working with the car and ramp to help you model the motion of the car with a distance vs. time graph. By measuring how long it takes the car to reach different points on the ramp, you be able to create a picture of the car's trip down the ramp Setting up the experiment l.
Acceleration - Wikipedia Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. At any point on a trajectory, the magnitude of the acceleration is given by the rate of change of velocity in both magnitude and direction at that point. The true acceleration at time t is found in the limit as time interval Δt → 0 of Δv/Δt Average Acceleration: Definition, Formula, Examples and more Once again, do not assume that the average acceleration for the whole is equal to the arithmetic mean of the average accelerations for the parts. ... Let's consider the instant the rocket is about to lift off to be 0 and label it as t 1. So, the velocity v 1 at instant t 1 is 0. t 1 = 0, v 1 = 0. Instantaneous Acceleration: Definition, Formula and more Often, to show how the acceleration of a particle changes over time, an acceleration vs time graph is used. Here's what an acceleration vs time graph might look like for a moving particle: Acceleration vs time graph; the acceleration at time 0 is 0, then becomes positive, and finally, at 9 seconds, it returns back to 0. Physics for Kids: Acceleration - Ducksters The average acceleration is the total change in velocity divided by the total time. This can be found using the equation a = Δv ÷ Δt. For example, if the velocity of an object changes from 20 m/s to 50 m/s over the course of 5 seconds the average acceleration would be: a = (50 m/s - 20 m/s) ÷ 5s a = 30 m/s ÷ 5s a = 6 m/s 2
What Is Acceleration - Formula, Unit, Examples, Types, FAQs - BYJUS Acceleration is defined as The rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Acceleration is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction. It is also the second derivative of position with respect to time or it is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. What is the Acceleration Formula? Motion Graphs: Position, Velocity & Acceleration (w/ Diagram) Motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. The three motion graphs a high school physics student needs to know are: position vs. time (x vs. t), velocity vs. time (v vs. t), and acceleration vs. time (a vs. t). The shapes of each graph relate by slope. Equations of motion - Wikipedia The differential equation of motion for a particle of constant or uniform acceleration in a straight line is simple: the acceleration is constant, so the second derivative of the position of the object is constant. 3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration - wikiHow 3. Use the formula to find acceleration. First write down your equation and all of the given variables. The equation is a = Δv / Δt = (vf - vi)/ (tf - ti). Subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity, then divide the result by the time interval. The final result is your average acceleration over that time.
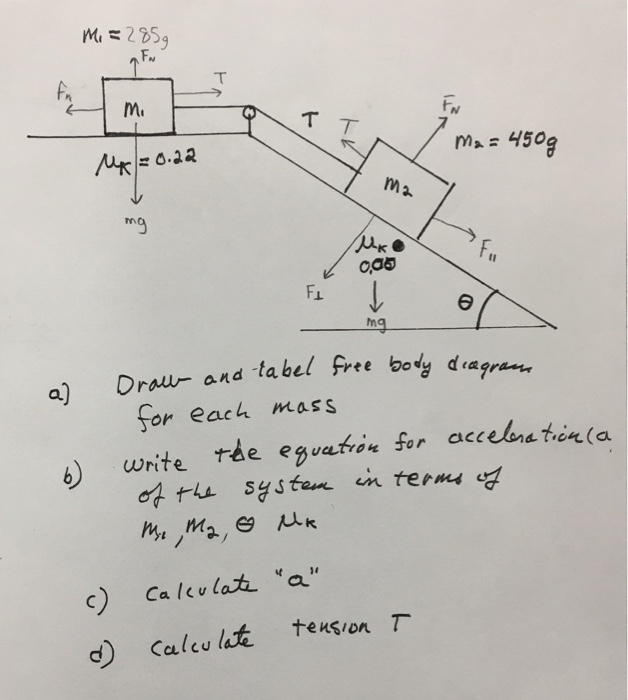
Finding Acceleration - Physics Classroom In this lesson, we will learn how to determine the acceleration of an object if the magnitudes of all the individual forces are known. The three major equations that will be useful are the equation for net force ( F net = m•a ), the equation for gravitational force (F grav = m•g), and the equation for frictional force (F frict = μ • F ...
Motion and forces - GCSE Combined Science Revision - BBC … GCSE Combined Science Motion and forces learning resources for adults, children, parents and teachers.
Linear Acceleration Formula: Definition, Concepts and Examples The formula for Linear Acceleration: Acceleration is the rate of change in the velocity towards the time change. We denote it by symbol a, and compute it as-. Linear Acceleration =. Its unit is meter per second squared or m . If t (time is taken), v (final velocity) and u (initial velocity) are provided. Then the acceleration formula:
How to Analyze Position, Velocity, and Acceleration with ... So, you differentiate position to get velocity, and you differentiate velocity to get acceleration. Here's an example. A yo-yo moves straight up and down. Its height above the ground, as a function of time, is given by the function, where t is in seconds and H ( t) is in inches. At t = 0, it's 30 inches above the ground, and after 4 seconds ...
How do you label force mass and acceleration? - Answers Newton's Second Law: Force = mass x acceleration. Solving for acceleration: acceleration = force / mass.Therefore, if you increase the mass, the same force will produce less acceleration.Newton's ...
Speed and Acceleration Flashcards | Quizlet How do you label acceleration? m/s^2 How do you graph acceleration? (speed versus time graph) Speed is increasing with time = acceleration, line is straight = acceleration is constant How do you graph acceleration? (distance versus time graph)
How do you label acceleration? - Answers How do you label force mass and acceleration? force: F, measured in newtons, N acceleration: a, measured in meters per second per second, ms-2. What are 3 kinds of acceleration?
Acceleration Time Graph - Understanding, Area and Examples - VEDANTU The area under curve = v. You can represent the change in velocity as v, change in acceleration as a and change in time as t. According to the definition of the acceleration, a = v/ t. By multiplying the t that is change in time interval to both sides, we get, a = v/ t. This is the direct theoretical formula which can be used to find any of the ...
How to Sketch Acceleration Time Graph From Velocity Time Graph NEXT Position displacement velocity acceleration Graph:
How To Format a Micro SD Card - PC Guide 22.06.2022 · The main reason you may want to do this is if a micro SD card has stopped working properly or it has corrupted. Formatting it can sometimes save it, which in turn saves you from having to buy a new one. Additionally, if the micro SD card is full, it is highly recommended that you format it if you want to re-use it.
Nsight Compute :: Nsight Compute Documentation 01.02.2022 · Select the target machine at the top of the dialog to connect and update the list of attachable applications. By default, localhost is pre-selected if the target matches your current local platform. Select the Attach tab and the target application of interest and press Attach.Once connected, the layout of NVIDIA Nsight Compute changes into stepping mode that allows you …
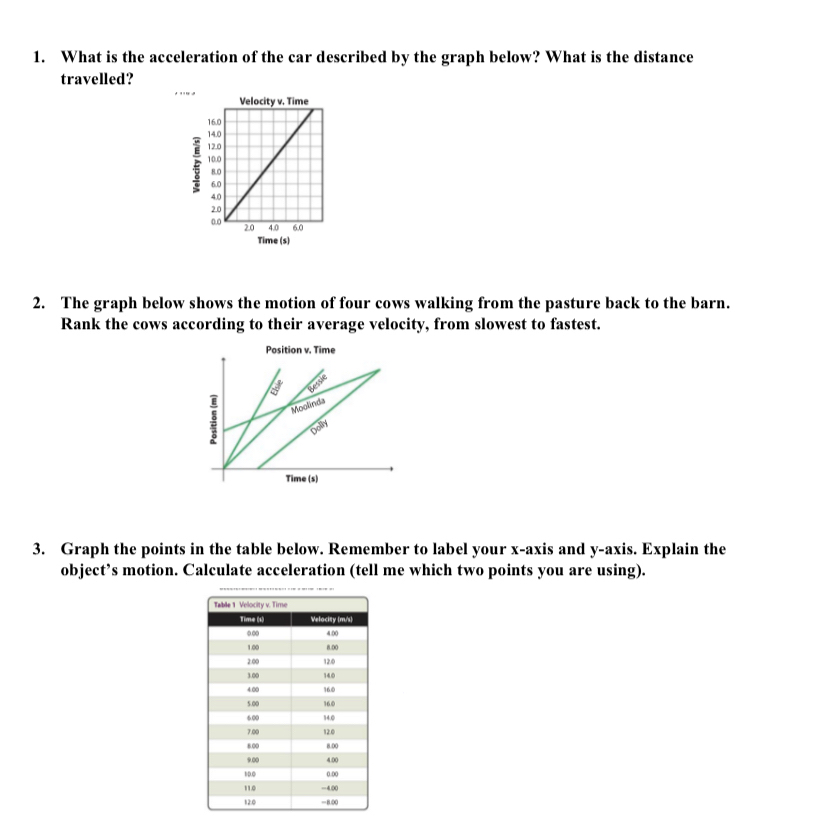
Velocity-time graphs - Speed, velocity and acceleration - BBC Acceleration can be calculated by dividing the change in velocity (measured in metres per second) by the time taken for the change (in seconds). The units of acceleration are m/s/s or m/s2. The...
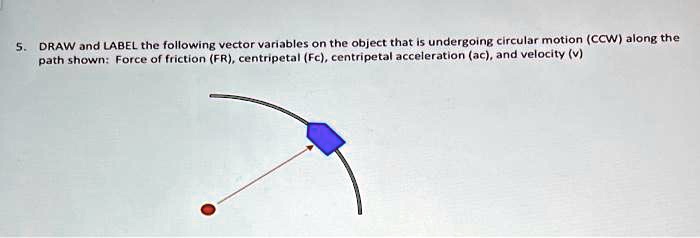
1-D Kinematics Problem: Ball Thrown Straight Up - UW-Green Bay When we drew the picture, we were careful to label each point of interest with a different subscript, and when we fill into the equation we need to be careful to fill in the correct value for the correct point. We cannot assume that values of zero go with the earlier point in times. In this expression, in fact, the velocity of zero occurs at the top of the motion (Point 2) rather than at …
3.2 Representing Acceleration with Equations and Graphs In the third kinematic equation, acceleration is the rate at which velocity increases, so velocity at any point equals initial velocity plus acceleration multiplied by time v = v 0 + a t Also, if we start from rest ( v 0 = 0 ), we can write a = v t 3.6 Note that this third kinematic equation does not have displacement in it.
How to Turn Off Mouse Acceleration on Windows 10 - How-To Geek 26.07.2021 · Mouse acceleration in Windows 10 is a feature that increases the distance and speed at which your cursor moves across the screen in response to the speed with which you move your physical mouse. With mouse acceleration enabled, if you were to quickly move your physical mouse three inches, your cursor could travel from one side of the screen to the other.
Configure hardware acceleration for the Android Emulator 18.08.2022 · The emulator runs best if it can use your machine’s hardware, such as the CPU, GPU, and modem, rather than run as pure software. This ability to use your machine’s hardware to improve performance is called hardware acceleration.The emulator can use hardware acceleration to improve your experience in two main ways: graphics acceleration, for …
How to Calculate Acceleration - dummies You can rearrange this equation with a little algebra to solve for acceleration; just divide both sides by t2 and multiply by 2 to get Great. Plugging in the numbers, you get the following: Okay, the acceleration is approximately 27 meters per second 2. What's that in more understandable terms?
Acceleration (video) | Khan Academy Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2). Acceleration is also a vector quantity, so it includes both magnitude and direction. Created by Sal Khan. Facebook Twitter Sort by:
Acceleration - Physics Classroom The average acceleration ( a) of any object over a given interval of time ( t) can be calculated using the equation This equation can be used to calculate the acceleration of the object whose motion is depicted by the velocity-time data table above. The velocity-time data in the table shows that the object has an acceleration of 10 m/s/s.
Spacecraft propulsion - Wikipedia Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry.. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages.
How to calculate tangential acceleration - 650.org How do you label tangential acceleration? Notations Used In The Formula a t is the tangential acceleration. Δv is the change in the angular velocity. Δt is the change in time. v is the linear velocity. s is the distance covered. t is the time taken. How do you convert tangential acceleration to angular acceleration? at=rΔωΔt a t = r Δ ω Δ t .





















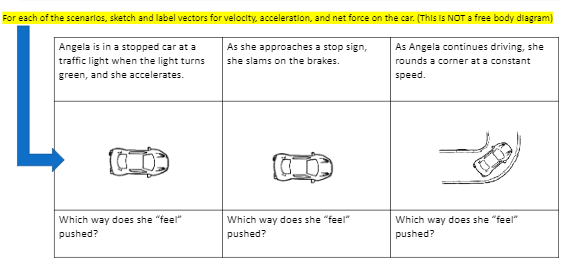



Post a Comment for "43 how do you label acceleration"