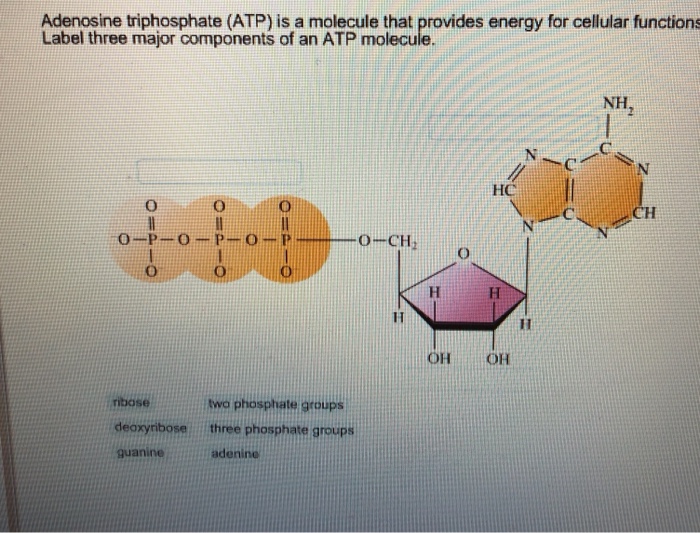
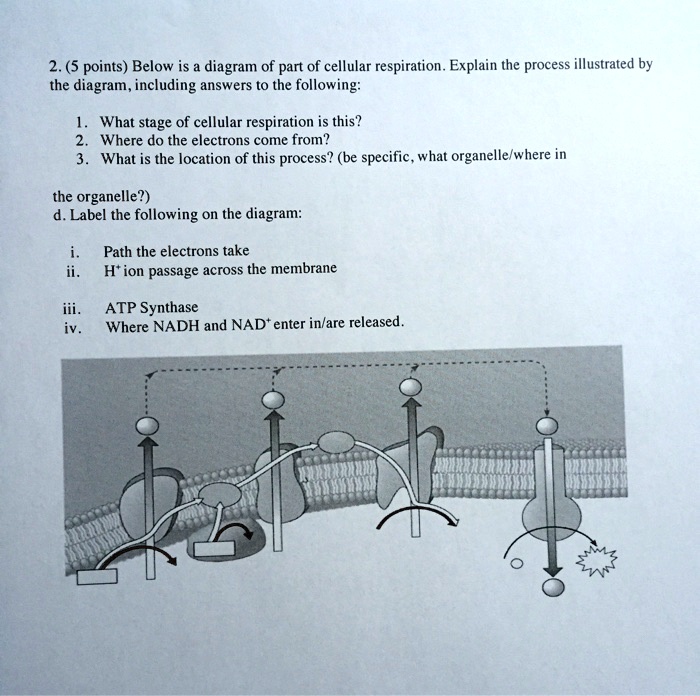
41 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M. Fatty acid - Wikipedia In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated.Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms …
7 draw atp and label each part of the molecule - coursehero.com 7 Draw ATP and label each part of the molecule including the base the ribose and. 7 draw atp and label each part of the molecule. School University of Texas; Course Title BCH 369; Type. Homework Help. Uploaded By saaminsz. Pages 4 This preview shows page 2 - 4 out of 4 pages.

Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
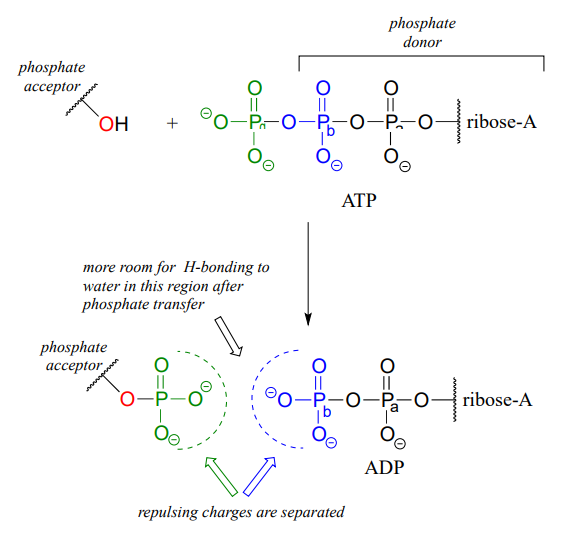
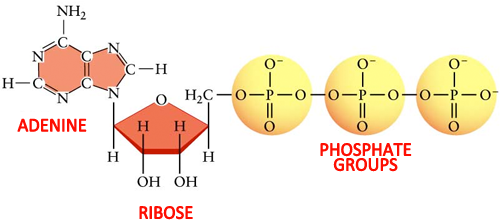
› 36111379 › DiFiores_Atlas_ofDiFiore's Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations ... Each chapter is also followed by review questions that can enable the reader to use them as self-assessment tools. The author strongly believes that this teaching material will play a crucial role in promoting the teaching-learning process through delivery of pertinent information to the trainees. Protein - Wikipedia Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid, for example AUG … 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
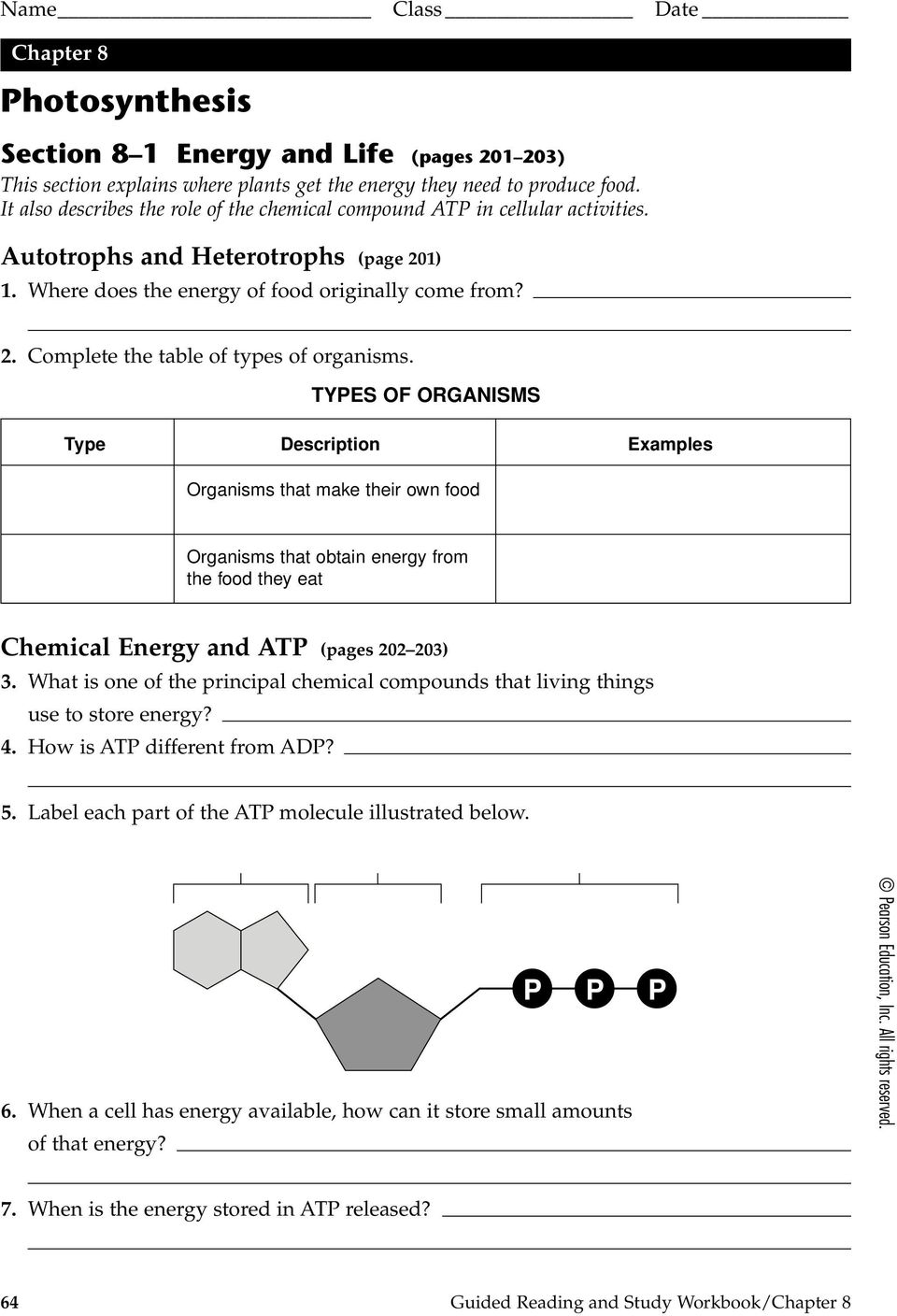
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. Describe the Three Parts of Atp Molecule - MaxkruwHendricks Based on the model of the ATP molecule above list the three parts of the ATP molecule and then label each on the simplified model of ATP shown below a. Refer to Model 1. Adenosine monophosphate AMP also called 5-adenylic acid has only one phosphate group. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples open.umn.edu › opentextbooks › textbooksBiology - 2e - Open Textbook Library Biology 2e is designed to cover the scope and sequence requirements of a typical two-semester biology course for science majors. The text provides comprehensive coverage of foundational research and core biology concepts through an evolutionary lens. Biology includes rich features that engage students in scientific inquiry, highlight careers in the biological sciences, and offer everyday ... What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
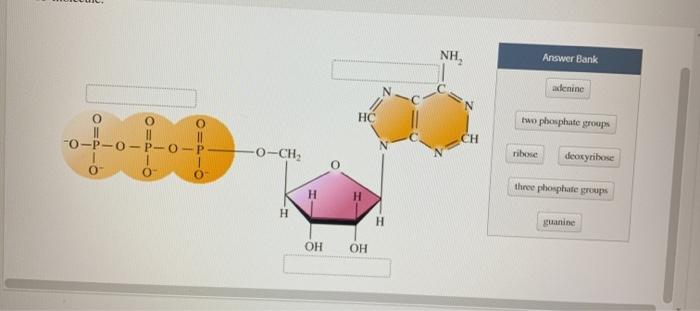
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Biology || Miss B Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? ... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the light-dependent reactions. a. ... ATP synthase allows H+ to pass through the protein, causing the protein to rotate. As it rotates, it Protein Digestion and Absorption – Nutrition: Science and … The mashed egg pieces enter the stomach from the esophagus. As illustrated in the image below, both mechanical and chemical digestion take place in the stomach. The stomach releases gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and the enzyme, pepsin, which initiate the chemical digestion of protein. Muscular contractions, called peristalsis ... › createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols; Chapter 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Within the image of ATP, label the three major parts of the molecule by dragging the labels to their targets. ... Groups: Chain of PO3's Ribose: Pentagon with OC2H2(OH)2 Adenine: pentagon and hexagon together with C's and N's This molecule is ATP, adenosine triphosphate. In this structural formula, in which the three phosphate groups are shaded ...
list three parts of the atp molecule and label each on the simplified ... List three parts of the atp molecule and label each on the simplified molecule - 10335111 MichaelChavezNumba18 MichaelChavezNumba18 05/30/2018 Biology Middle School answered List three parts of the atp molecule and label each on the simplified molecule 1 See answer Advertisement Assignment Essays - Best Custom Writing Services Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. (PDF) Bioprocess Engineering-Basic Concepts by Shuler and Kargi ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. › books › NBK26837Isolating, Cloning, and Sequencing DNA - Molecular Biology of ... In this way “DNA probes” containing many labeled nucleotides can be produced for nucleic acid hybridization reactions (discussed below). The second procedure uses the bacteriophage enzyme polynucleotide kinase to transfer a single 32 P-labeled phosphate from ATP to the 5′ end of each DNA chain (Figure 8-24B).
DiFiore's Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations (11th … Each chapter is also followed by review questions that can enable the reader to use them as self-assessment tools. The author strongly believes that this teaching material will play a crucial role in promoting the teaching-learning process through delivery of pertinent information to the trainees. Nevertheless, constructive comments and ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and ... Glucose metabolism: fueling the brain. The mammalian brain depends on glucose as its main source of energy. In the adult brain, neurons have the highest energy demand [], requiring continuous delivery of glucose from blood.In humans, the brain accounts for ~2% of the body weight, but it consumes ~20% of glucose-derived energy making it the main consumer of …
› 80127975 › Bioprocess_Engineering(PDF) Bioprocess Engineering-Basic Concepts by Shuler and ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
› pmc › articlesSugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and ... The role of glucose for brain function. Glucose (Glc) is the main source of energy for the mammalian brain, (a) Specialized centers in the brain, including proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons in the hypothalamus, sense central and peripheral glucose levels and regulate glucose metabolism through the vagal nerve as well as neuroendocrine signals..
Photosynthesis_Worksheet_11.doc - ATP/Photosynthesis... View Photosynthesis_Worksheet_11.doc from BIOLOGY 287 at Woodbury High School, Minnesota. ATP/Photosynthesis Worksheet Name _ Hr. _ 1. Label the parts of the molecule below. 2. Of the parts
PDF Photosynthesis Study Guide - All-in-One High School Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? ATP and Glucose 8. Circle the letter of molecules used to regenerate the energy in ATP. a.
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, whereas ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples

circle use the figure nucleotide is 5 the purines write the carbons 1 5 below to 3 figure and which side is on the the following 1 belco5 use 1 to show which 1 41068
8.1 Energy and Life Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) compound that cells use to store and release energy Primary Producer 1st producers of energy rich compounds Consumer rely on other organisms for their energy needs and food supply Food Chain flow of energy through the ecosystem by the process of eating and being eaten Autotroph organisms that make their own food
Biology - 2e - Open Textbook Library Biology 2e is designed to cover the scope and sequence requirements of a typical two-semester biology course for science majors. The text provides comprehensive coverage of foundational research and core biology concepts through an evolutionary lens. Biology includes rich features that engage students in scientific inquiry, highlight careers in the biological sciences, and offer …
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life - Decatur Public Schools District 61 Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, whereas ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples
Isolating, Cloning, and Sequencing DNA - Molecular Biology of the … Gel Electrophoresis Separates DNA Molecules of Different Sizes. The length and purity of DNA molecules can be accurately determined by the same types of gel electrophoresis methods that have proved so useful in the analysis of proteins. The procedure is actually simpler than for proteins: because each nucleotide in a nucleic acid molecule already carries a single negative …
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
What are the three parts of the ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and ...
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ProteinProtein - Wikipedia Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid, for example AUG (adenine–uracil–guanine) is the code for methionine.
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
Protein - Wikipedia Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid, for example AUG …
› 36111379 › DiFiores_Atlas_ofDiFiore's Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations ... Each chapter is also followed by review questions that can enable the reader to use them as self-assessment tools. The author strongly believes that this teaching material will play a crucial role in promoting the teaching-learning process through delivery of pertinent information to the trainees.


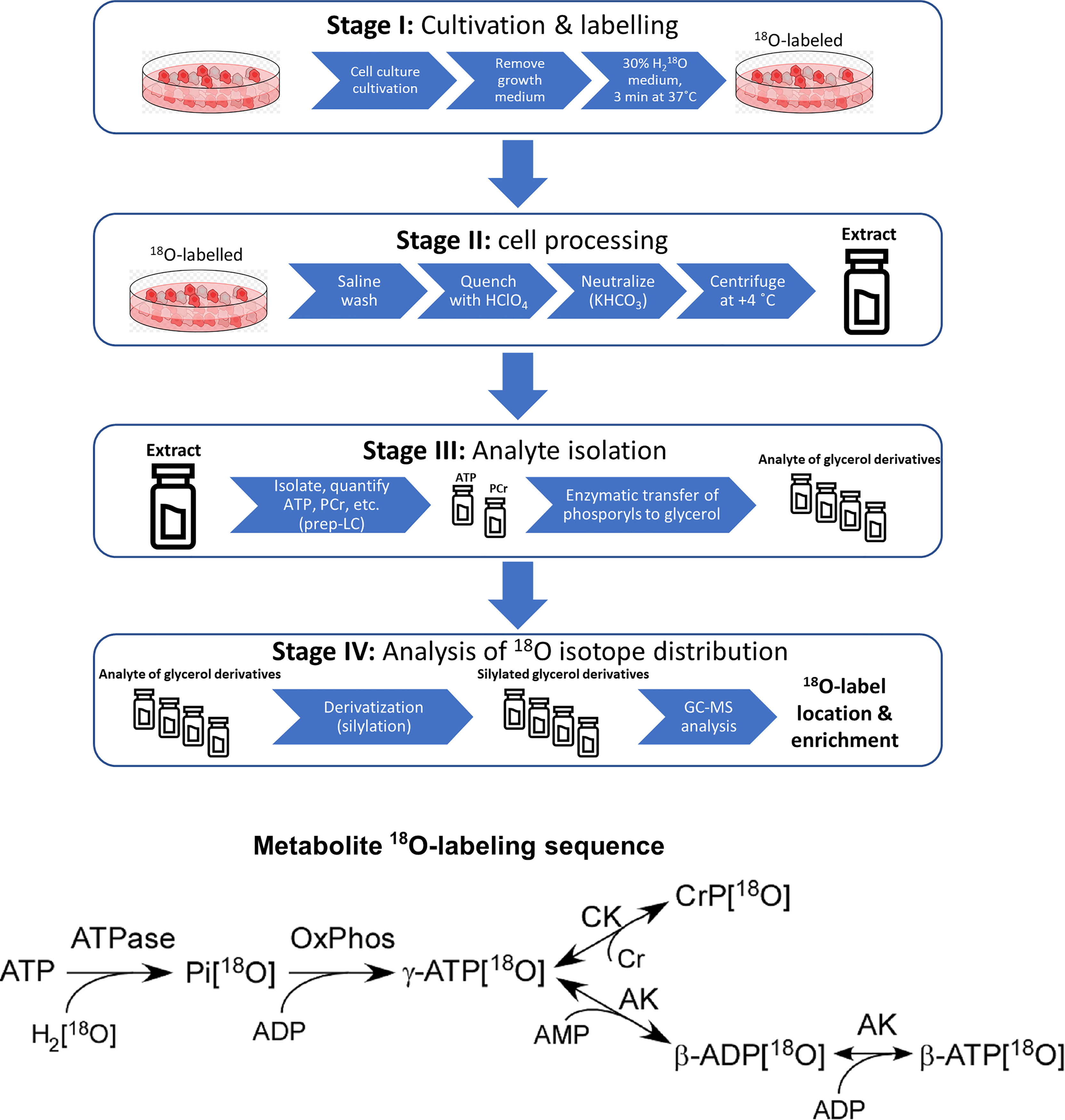

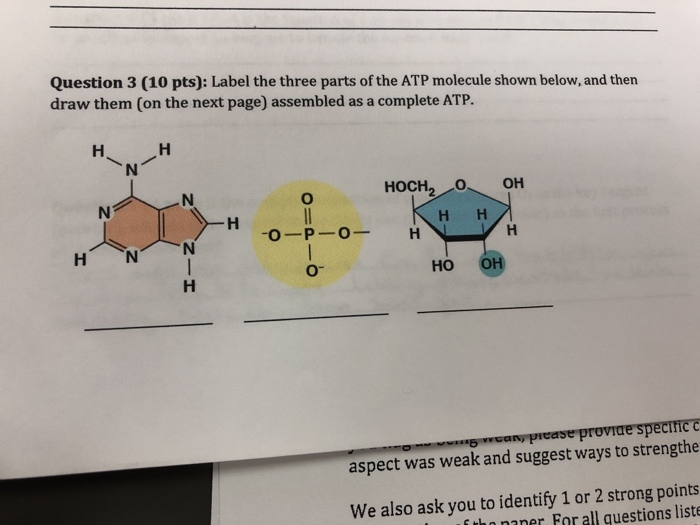











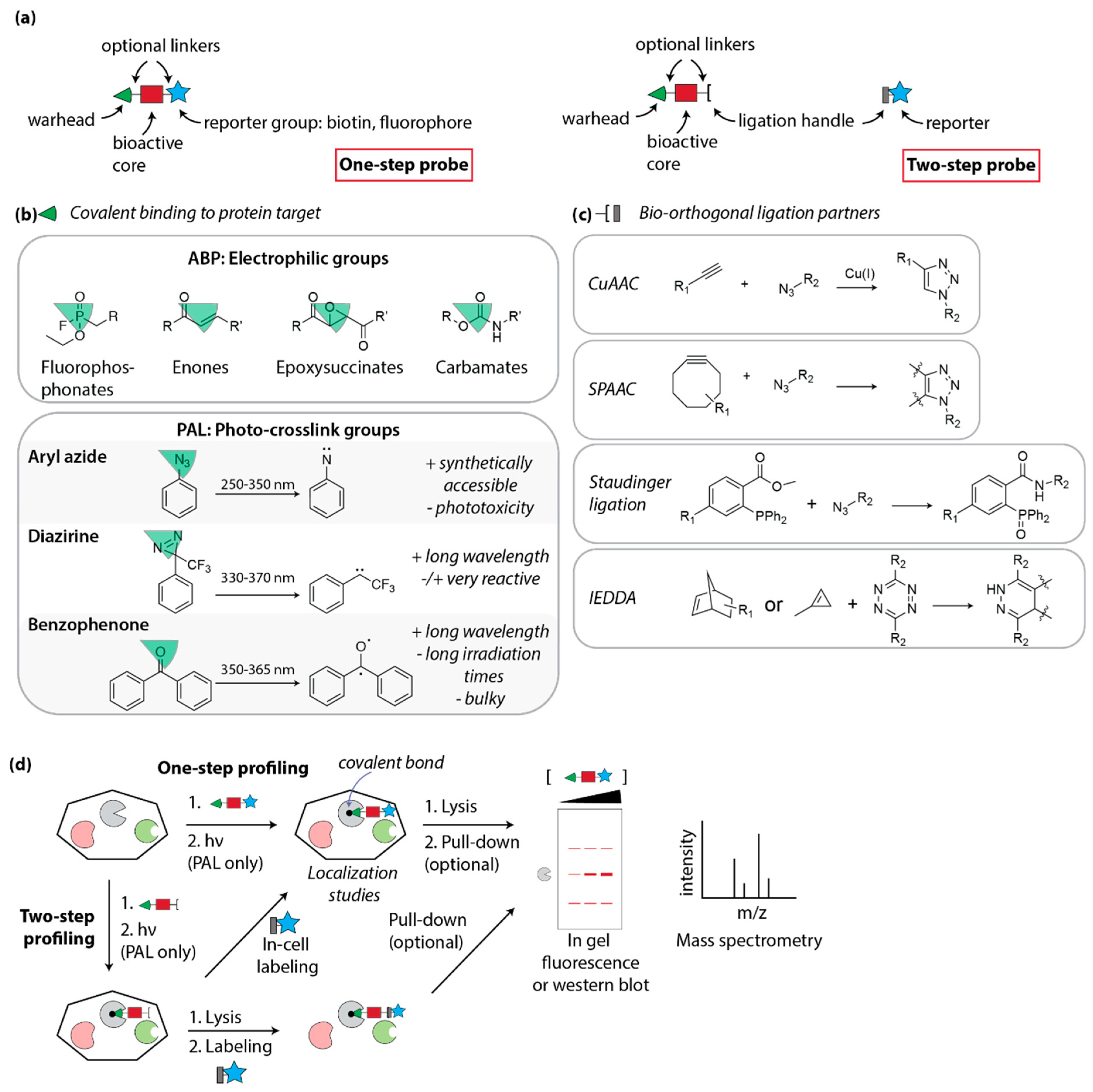





Post a Comment for "41 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below"